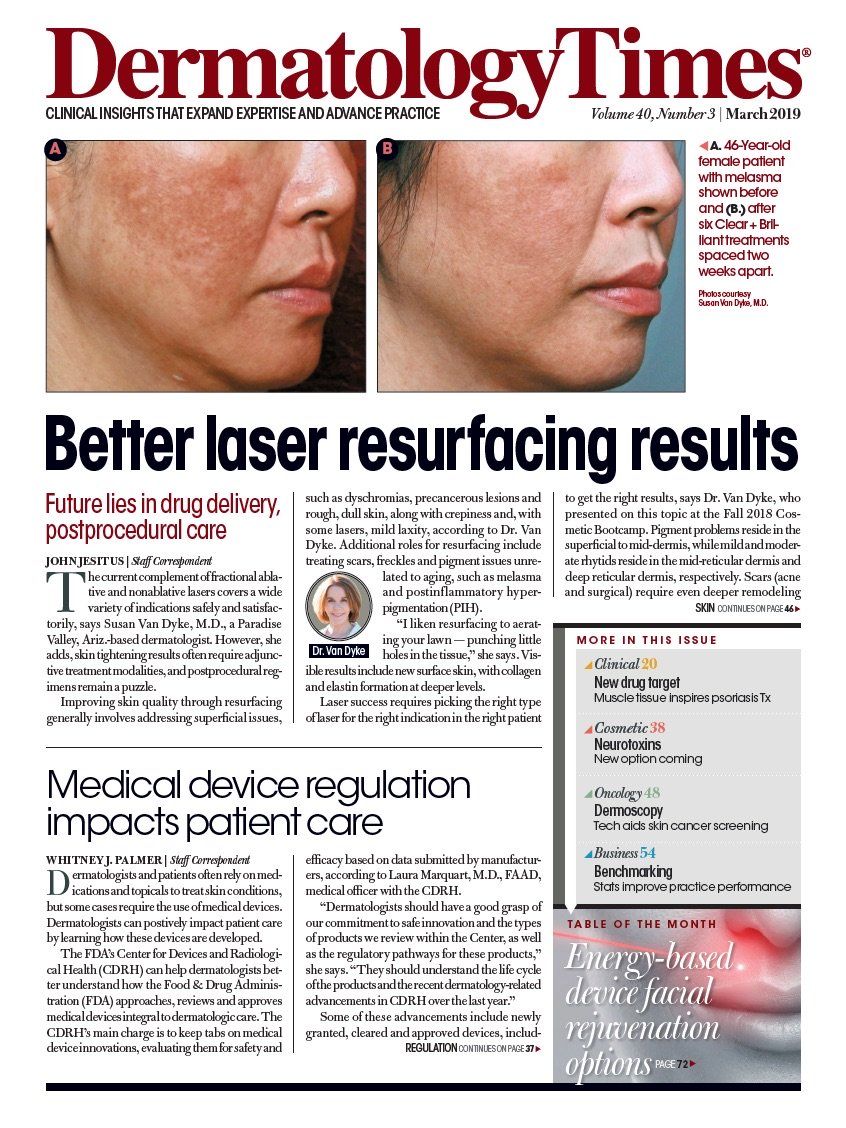
- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
Publication
Article
Dermatology Times
RT002 performs well in late-phase study
Author(s):
Revance Therapeutics announced in early December that its longacting neuromodulator daxibotulinumtoxinA for Injection RT002 delivered positive results in a phase 3 study for treatment of moderate-to-severe glabellar lines.
Longacting neuromodulator daxibotulinumtoxinA delivered positive results in a phase 3 study for treatment of moderate-to-severe glabellar lines. (ladyalex - stock.adobe.com)
Revance Therapeutics announced in early December that its longacting neuromodulator daxibotulinumtoxinA for Injection RT002, which features the company’s proprietary stabilizing excipient peptide technology, delivered positive results in a phase 3 study for treatment of moderate-to-severe glabellar lines. Use of RT002 was well-tolerated in more than 3,800 treatments studied, and the average time to return to baseline glabellar line severity was 28 weeks, according to a Revance news release.
“Revance is entering 2019 with tremendous momentum on multiple fronts,” says Dan Browne, president and chief executive officer at Revance in a company press release. “We have an exciting ensemble of late-stage clinical trials underway for our next-generation neuromodulator and are operating a U.S.-based, commercial-scale drug substance and drug product facility to manufacture a broad range of proprietary neuromodulation formulations. We also have an active collaboration for the introduction of RT002 in China and another to develop a biosimilar to Botox. Strategically, as we anticipate entering the market with RT002 in 2020, we intend to set a new standard in neuromodulators, focused on providing patients with the ability to safely alleviate the appearance of frown lines with just two or fewer treatments per year.”
Reference:
Revance’s RT002 Demonstrates Unprecedented Efficacy and Duration In Largest-Ever Aesthetic Neuromodulator Clinical Program. December 4, 2018. Available at: https://investors.revance.com/news-releases/news-release-details/revances-rt002-demonstratesunprecedented-efficacy-and-duration. Accessed February 2019.