- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
Opinion
Video
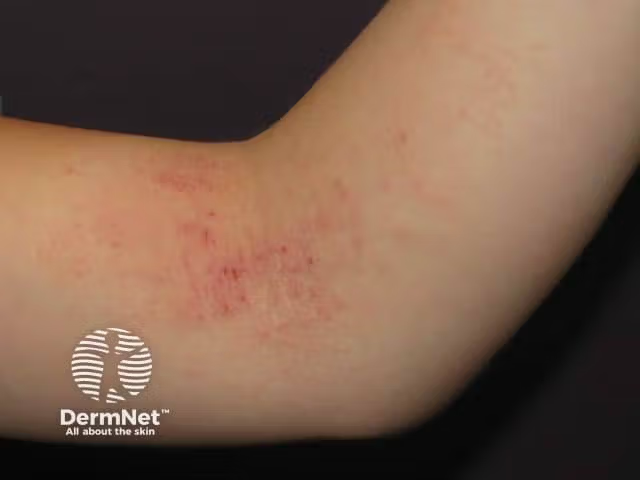
Understanding Efficacy and Real-World Application of Topical Non-Steroidal Treatments for AD
Author(s):
Dr James Del Rosso underscores the importance of phase 2 and dose-ranging studies to uncover efficacy differences between therapies, while the panel explores how clinical data from ruxolitinib trials mirrors real-world outcomes.
This is a video synopsis of a discussion involving James Del Rosso, DO, dermatologist in Las Vegas, Nevada, Brad Glick, DO, MPH, FAAD, a principal investigator at GSI Clinical Research in South Florida, and Lisa Swanson, MD, FAAD, a dermatologist and pediatric dermatologist in Boise, Idaho.
The panelists delve into comparative studies examining the efficacy of topical therapies for atopic dermatitis (AD), particularly focusing on the comparison between triamcinolone (0.1% cream) and topical ruxolitinib. Dr. Del Rosso highlights findings from a phase two study where different strengths and frequencies of applications were evaluated.
Surprisingly, the study revealed that topical ruxolitinib outperformed triamcinolone in terms of reducing the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EZ) score and Investigator's Global Assessment (IGA) response. The data showed a higher IGA response rate (38%) with ruxolitinib compared to triamcinolone (26%), indicating the superior efficacy of ruxolitinib in managing AD symptoms.
Furthermore, Dr. Glick emphasizes the real-world applicability of these findings, noting that topical ruxolitinib not only demonstrates efficacy in clinical trials but also translates into significant improvements in patients' quality of life. He shares anecdotal evidence of patients experiencing rapid relief from itching and improved skin condition with topical ruxolitinib, highlighting its clinical effectiveness.
Dr. Swanson underscores the importance of topical ruxolitinib's cosmetic elegance, particularly for patients with tactile sensitivity associated with AD. She praises its soothing properties, noting that it provides relief without causing burning or stinging sensations upon application.
Overall, the discussion underscores the paradigm shift in AD management, with topical ruxolitinib emerging as a promising therapeutic option that offers rapid and effective relief from AD symptoms, including itching and skin inflammation.
Video synopsis is AI-generated and reviewed by Dermatology Times® editorial staff.