- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
Article
Quiz: Case studies in psoriasis
Author(s):
Test your knowledge by answering these five questions about different psoriasis cases.
(©Sweetheart/Shutterstock.com)
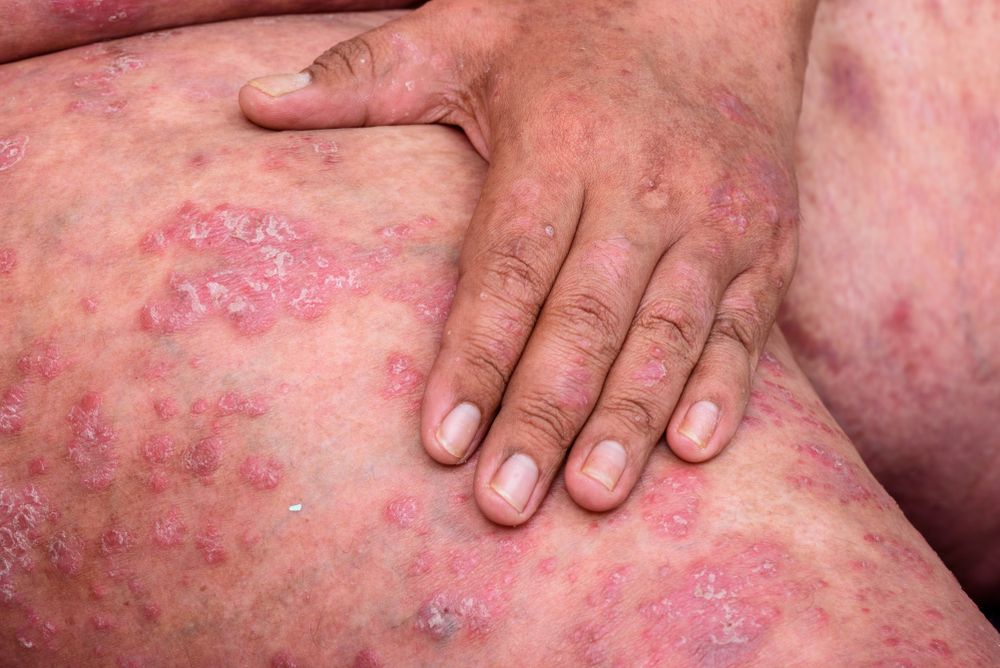
1. A 47 year old man presents to the dermatology clinic complaining of a pruritic rash on his scalp and his umbilicus. The physical exam shows there are erythematous plaques with silvery scales consistent with psoriasis. Counseling on the management of psoriasis is initiated. According to the Joint AAD-NPF guidelines, what other factors should the dermatologist consider?
A. Clinicians should consider early and more frequent screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia in psoriasis patients who are candidates for systemic or phototherapy or who have psoriasis involving >10% of the BSA.
B. CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia) with national guidelines is recommended for all patients with psoriasis.
C. CV risk management in psoriasis for hypertension and dyslipidemia should be carried out according to national guidelines. The target for blood pressure and lipid levels are based on risk calculated for psoriasis. Antihypertensives and statins may be used as in the general population. CV risk management should be performed by either a primary care physician or other health care provider experienced in CV risk management or the dermatologist.
D. Risk score models should be adapted for patients with psoriasis by introducing a 1.5 multiplication factor when the patient with psoriasis meets either criteria: disease severity of BSA >10% or candidate for systemic or phototherapy
E. All of the above
Click to the next page for the answer.
Answer: E. All of the above
Reference: Elmets, Craig A., et al. "Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with awareness and attention to comorbidities." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 80.4 (2019): 1073-1113.
2. A 45 year old woman was referred to dermatology with plaque psoriasis. While obtaining a history she states that prior to developing a rash she suffered from back pain for 4 years associated with nighttime awakening, and morning stiffness lasting 60 minutes. What percentage of psoriasis present with antecedent psoriatic arthritis?
A. 10%
B. 20%
C. 30%
D. 40%
Click to the next page for the answer.
Answer: B. 20%
Reference: Alonso, JC Torre, et al. "Psoriatic arthritis (PA): a clinical, immunological and radiological study of 180 patients." Rheumatology 30.4 (1991): 245-250.
3. A 27 year old woman with a history of multiple sclerosis and crohn disease presents with severe plaque psoriasis that has not responded to dmards or phototherapy. Which of the following medications would be preferred?
A. Etanercept
B. Adalimumab
C. Ustekinumab
D. Secukinumab
Click to the next page for the answer.
Answer: C. Ustekinumab
Reference: Feagan, Brian G., et al. "Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease." New England Journal of Medicine 375.20 (2016): 1946-1960.
4. A 74 year old man with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis status post treatment with adalimumab, infliximab and etanercept, presents with active psoriasis. She inquires about starting a interleukin 17 inhibitor. Which of the following is not a interleukin 17 inhibitor?
A. Guselkumab
B. Brodalumab
C. Secukinumab
D. Ixekizumab
Click to the next page for the answer.
Answer: A. Guselkumab
Reference: Sofen, Howard, et al. "Guselkumab (an IL-23–specific mAb) demonstrates clinical and molecular response in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis." Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 133.4 (2014): 1032-1040.
5. A 76 year old woman treated with Adalimumab for psoriasis is scheduled for cataract surgery. Her ophthalmologist asks how to proceed with her adalimumab for this low risk procedure. What is the appropriate recommendation?
A. Stop adalimumab 6 weeks before surgery
B. Stop adalimumab 4 weeks before surgery
C. Stop adalimumab 2 weeks before surgery
D. Don’t stop adalimumab
Click to the next page for the answer.
Answer: D. Don’t stop adalimumab
Reference: Menter, Alan, et al. "Joint AAD-NPF guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with biologics." Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 80.4 (2019): 1029-1072.





