- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
News
Article
Dupilumab Plus Antihistamines Beats Antihistamines Alone in Treating CSU
Author(s):
Patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria saw improvement in itch and hive severity when dupilumab was added to their antihistamines in a 24-week study.
Pol Maria/AdobeStock
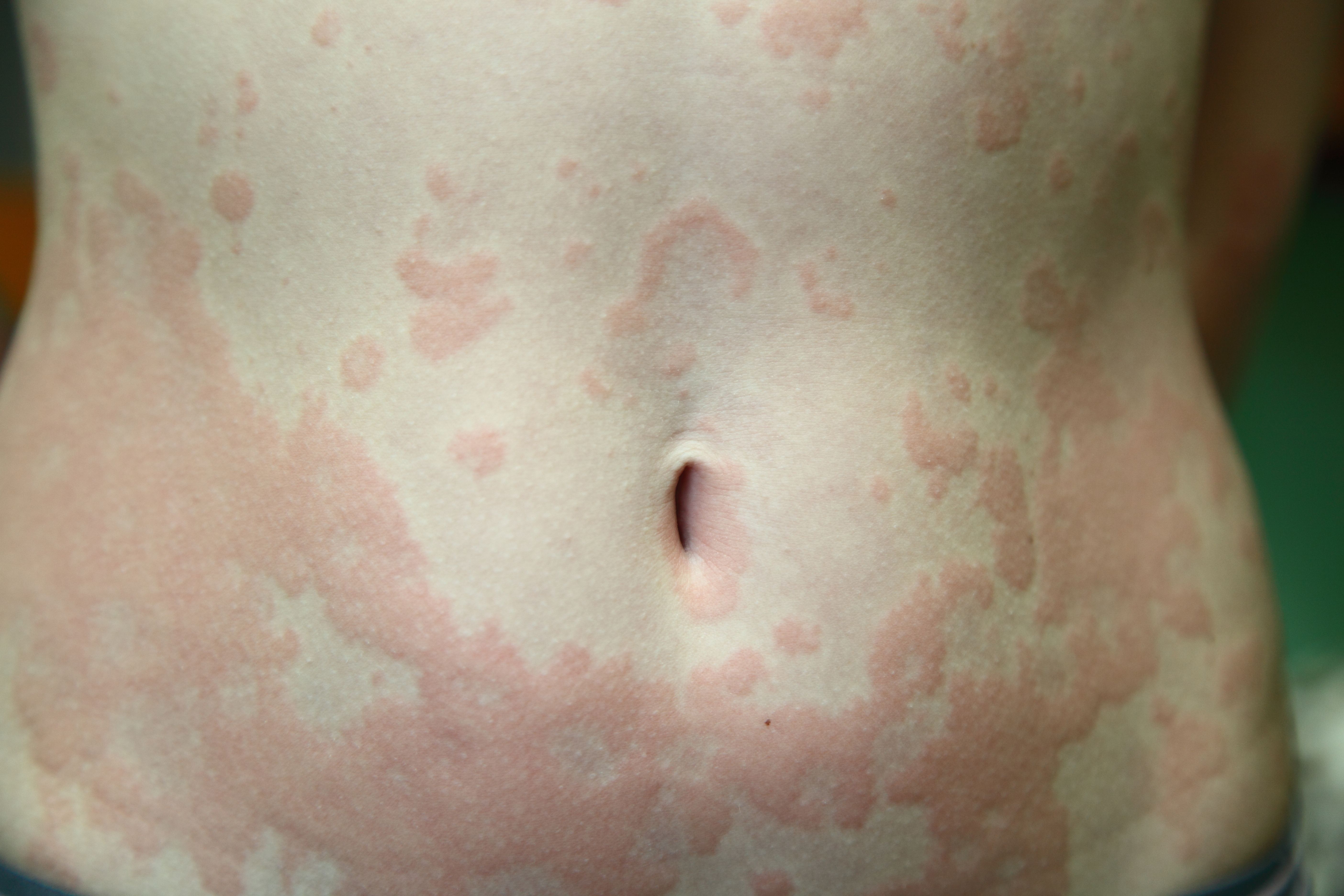
The combination of dupilumab (Dupixent)plus standard-of-care antihistamines improves chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) better than antihistamines alone, researchers recently reported in a poster at the Maui Derm Hawaii 2024 conference in Wailea, Hawaii.1
The researchers performed a randomized, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 trial in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria who remained symptomatic despite treatment with standard-of-care (SoC) H1-antihistamines.2
The patients were randomized to receive add-on dupilumab (dupilumab/SoC) or placebo (placebo/SoC) subcutaneously every 2 weeks for 24 weeks. The add-on dupilumab dosing was 300 mg in adults and adolescents ≥60 kg, and 200 mg in adolescents <60 kg and children ≥30 kg.
Improvement was measured using the Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days (UAS7), Itch Severity Score over 7 days (ISS7), and Hives Severity Score over 7 days (HSS7) in each arm of the study.
The patients in the trial were aged ≥6 years; had received a diagnosis of CSU >6 months prior to screening visit; had had presence of itch and hives for >6 consecutive weeks despite H1-antihistamine use; had UAS7 and ISS7 scores of ≥16 and ≥8; and were omalizumab-naïve.
At week 24, the poster authors wrote, more patients experienced UAS7, ISS7, and HSS7 improvements with dupilumab and antihistamines than with placebo and antihistamines. Specifically, 74.2% of patients receiving dupilumab and antihistamines achieved ≥11-point reductions in UAS7, while 50.0% of patients receiving placebo and antihistamines did, according to the poster.
Similarly, 78.8% of patients receiving dupilumab and antihistamines reached ≥5-point reductions in ISS7 and HSS7, vs 51.7% of patients receiving placebo and antihistamines.
The poster authors concluded, “Irrespective of within-patient responder thresholds, greater proportions of patients experienced improvement in UAS7, ISS7, and HSS7 with dupilumab/SoC vs placebo/SoC at Week 24.”
Investigators also wrote, “Overall safety was consistent with the known dupilumab safety profile.”
Data included in the poster were originally presented at the Annual American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Meeting (ACAAI), November 9–13, 2023, in Anaheim, California.
The research was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
References
- Beck LA , Casale TB, Mortensen E, et al. Dupilumab demonstrates greater improvement in disease activity than standard-of-care h1-antihistamines in CSU. Poster presented at: Maui Derm Hawaii 2024; January 22-26, 2024; Wailea, Maui, HI.
- Maurer M, Casale TB, Saini S, et al. Dupilumab significantly reduces itch and hives in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria: results from a phase 3 trial (LIBERTY-CSU CUPID Study A). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022;149(2).DOI:10.1016/j.jaci.2021.12.002






