- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
News
Article
Dermoscopy Assessment Showed Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A in Egyptian Patients With Androgenetic Alopecia
Author(s):
BTA treatment was both safe and effective in male and female patients, indicating its potential as a therapeutic strategy in treating Egyptian patients with AGA.
In a cohort of male and female patients from Egypt with androgenetic alopecia (AGA), varying concentrations of botulinum toxin A (BTA) was safe and effective, indicating its potential as a therapeutic strategy for hair loss treatment in the Egyptian population.
boyloso/Adobe Stock
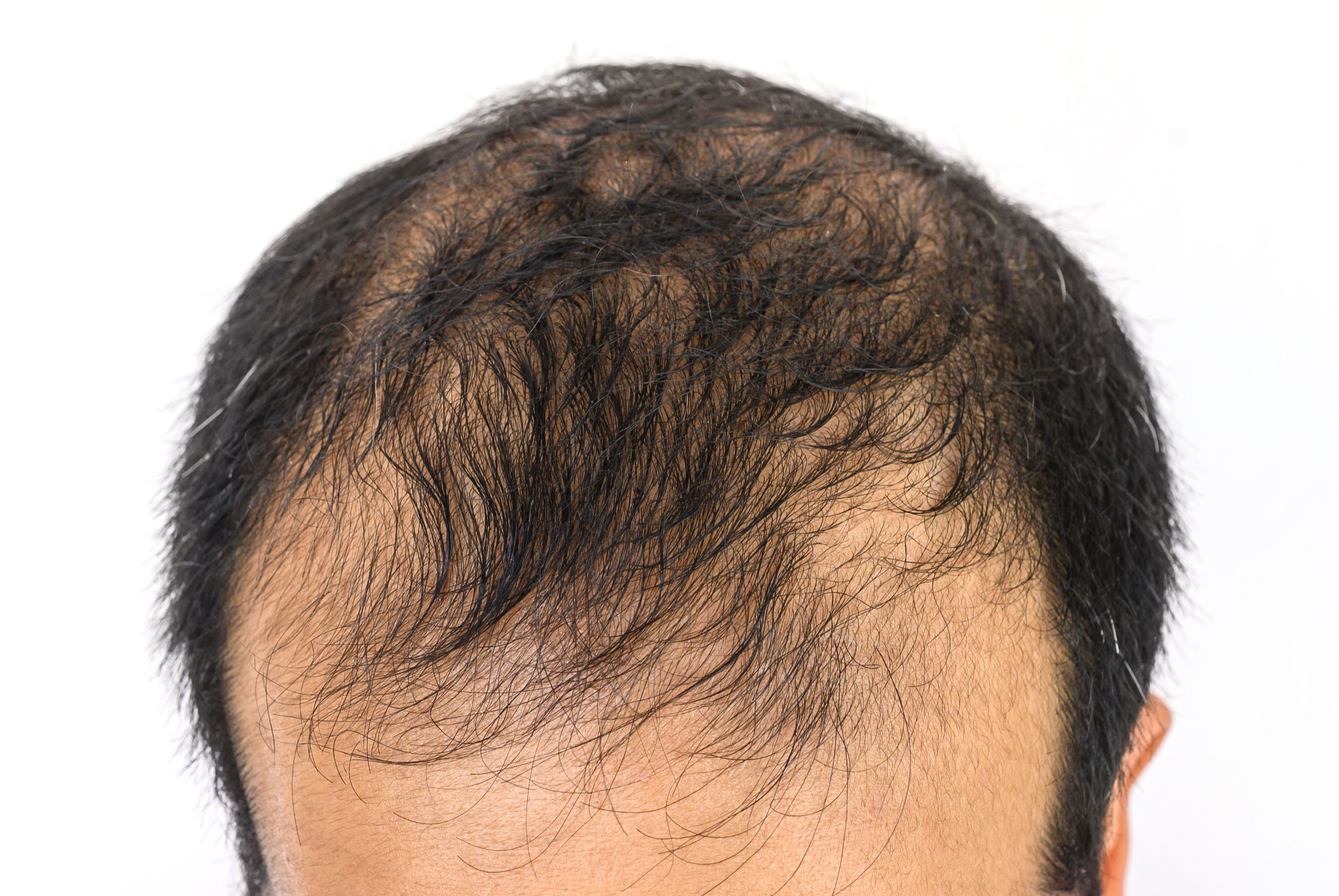
According to a recent study1 published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, investigators Seoudy et al sought to evaluate and compare the efficacy of 2 concentrations of BTA injections in patients with AGA. Existing research,2 for example, has shown a significant lack of public awareness and consistent treatment for alopecia areata in the Middle East and Africa.
Adult patients between the ages of 18 and 50 with AGA who visited the Memorial Souad Kafafi University Hospital between June and November 2022 (n=32) were considered for participation. All patients had received a diagnosis from a physician which had been confirmed by dermoscopy. This sample size, according to investigators, was determined by a previous study process, basing the number of participants on average hair count before and after treatment with BTA.
In males, participants were required to meet criteria for Norwood-Hamilton classifications I through VII. Female participants met Ludwig classifications I through III criteria in order to participate in the study. Any patients who were pregnant or lactating, had received Botox injections within the past 3 months, had received systemic treatment within the past 3 months (antimalarials, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, NSAIDS), a history of severe systemic or otherwise related diseases, or who were currently undergoing treatment for hair fall, were excluded from participation.
Prior to receiving treatment, all participants provided relevant demographic information, disease-specific information, and underwent several assessments, including a quality of life (QoL) assessment and clinical, general, and local examinations.
At the time of treatment, patient vertexes were sterilized and divided equally down the middle into 2 distinct treatment sections. On the left treatment side, patients received approximately 3.3 units of Botox per site with a dilution of 100 U/3 mL with 0.9% normal saline. On the right treatment side, patients received approximately 2.5 units of Botox per site with a dilution of 100 U/4 mL with 0.9% normal saline.
After treatment, patients were instructed not to lay down and avoid pressure or massage for 6 hours. They were also instructed to avoid exercise or excessive sun exposure.
Participants’ scoring using the Norwood-Hamilton and Ludwig classifications had significantly improved after treatment. The rate of female patients with a Grade 1 classification had risen from 14.8% before treatment to 70.4% after 6 months. In male patients, the number of patients with a Grade 2 classification rose from 0% to 60% in 6 months.
Dermoscopic findings at months 3 and 6 after treatment indicated transformations in vellus hair, hair diversity, and perifollicular signs. Overall, 56.2% of patients reported satisfaction with the treatment outcomes, with 25% of patients reporting that the right side had a better appearance as a result.
Adverse effects included headache, pain, nausea, and site irritation.
“The results of the present study showed that BTA injections of 33.3 U/3 mL (in 0.9% normal saline) concentration are safe and showed statistically significant results in AGA patients of both genders,” according to study authors Seoudy et al. “These findings offer a cutting-edge conceptual structure and therapeutic strategy for the management of AGA in Egyptian population.”
References
- Seoudy WM, Metwally OA, Elfangary MM, Mohamed TM. Assessment of efficacy of different botulinum toxin a concentrations in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia assessed by dermoscopy. J Cos Dermatol. Published online August 31, 2023. doi:10.1111/jocd.15972
- Al Hammadi A, Parmar NV, Aljefri K, etal. Review on alopecia areata in the Middle East and Africa: Landscape and unmet needs. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023;13(7):1435-1464. doi:10.1007/s13555-023-00946-8





