- Case-Based Roundtable
- General Dermatology
- Eczema
- Chronic Hand Eczema
- Alopecia
- Aesthetics
- Vitiligo
- COVID-19
- Actinic Keratosis
- Precision Medicine and Biologics
- Rare Disease
- Wound Care
- Rosacea
- Psoriasis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Melasma
- NP and PA
- Skin Cancer
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa
- Drug Watch
- Pigmentary Disorders
- Acne
- Pediatric Dermatology
- Practice Management
- Prurigo Nodularis
- Buy-and-Bill
News
Article
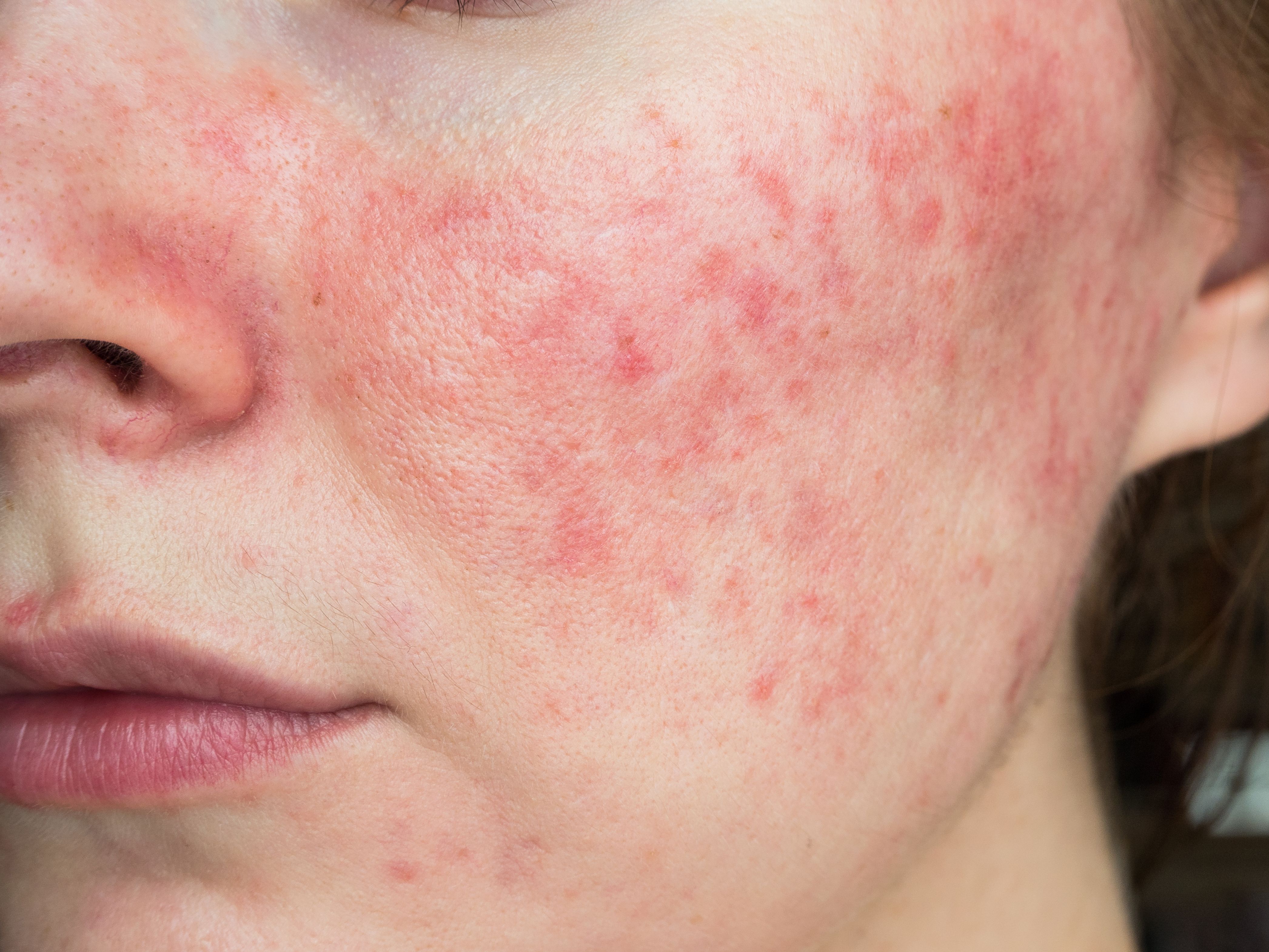
Could Tranexamic Acid Be Key to Treating Rosacea?
Author(s):
A recent review found the antifibrinolytic drug performed well in several clinical studies, none of which reported severe adverse events.
Image Credit: © Svetlana - stock.adobe.com

Despite its prevalence, the precise pathophysiology of rosacea remains unknown, with novel pharmacological therapies currently under investigation. A recent review investigated the efficacy of tranexamic acid (TA), a synthetic, lysine-like compound that competitively inhibits fibrinogen production by synthesizing fibrinolytic enzymes, for treatment of rosacea. Researchers found all studies included in the review demonstrated the potential of TA for the treatment of rosacea by regulating skin barrier function and immune reactions, as well as reducing angiogenesis.1
Background
Although little is known about the pathophysiology of rosacea, it is hypothesized that it could be associated with genetic background, abnormal innate and adaptive immunity, dysregulated neurovascular system, impaired skin barrier function, and an altered microbiome.2 While there are several treatment options available for patients with rosacea, an optimized therapy that effectively targets both inflammation and post-inflammatory pigmentation is needed. TA is an antifibrinolytic drug first introduced in the 1970s to treat melasma and has since been used to treat post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, Riehl’s melanosis, acne-related erythema, chronic urticaria, and angioedema. According to researchers behind this review, there is a growing amount of evidence suggesting that TA is effective in treating rosacea.
After an extensive search through PubMed and Web of Science, researchers found 6 studies published between 2012 and 2023 that met the criteria for inclusion in the review. All 6 estimated the therapeutic effects of TA for rosacea following various techniques: Intradermal injections, oral medications, topicals, microneedling, and laser-assisted delivery.
Topical Treatment
In 3 out of 6 studies, topical TA was used as monotherapy. In a2012 study, researchers reported 6 patients with irritant contact dermatitis and papulopustular rosacea were treated with a topical 10% TA solution once or twice a week. They observed significant reductions in erythema and symptoms such as itching, flushing, and burning.3 Similarly, aretrospective study of 30 patients with rosacea prescribed patients a topical 5% TA solution twice daily for 2 weeks. After the 14-day period, researchers stated fewer inflammatory lesions were observed. The study also reported that skin biophysical functions, such as trans-epidermal water loss, skin surface pH, and stratum corneum hydration improved “remarkably” following treatment.4
A 2019 study included in the review used a topical 10% TA solution in patients diagnosed with erythematotelangiectatic steroid-induced rosacea and melasma. Researchers reported an improvement in the severity of erythema, telangiectasia, and burning sensation after the solution was administered twice daily for 4 to 6 weeks.5 Finally, researchers included a 2018 clinical trial comparing the effects of 10% TA alone versus with the combination of 10% TA and microneedling. They found significant improvements in the clinical severity and quality of life in both groups. The study noted that in the combination group some adverse effects caused by microneedling were observed, subsiding shortly after the procedure.6
Systemic and Assisted Delivery Treatments
A 2016 study included in the review found that a combination of 250 mg oral TA, 40 mg propranolol, and 50 mg minocycline daily improved erythema and subjective symptoms in one patient with rosacea.7 The last study incorporated into the review found that intradermal microinjection of 5% TA solution significantly reduced the investigator’s global assessment of rosacea severity score. Researchers noted that clinical improvements were maintained for at least 3 months after treatment.8
Key Takeaways and Future Research Opportunities
In the 6 clinical studies included in the review, TA was reported as effective in treating rosacea. Each reported minimal adverse effects, mainly transient skin reactions such as erythema and irritation. Although promising, researchers suggested that further robust, randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes are necessary to confirm TA's efficacy, optimal dosing, long-term outcomes, and potential synergies with other treatments. They are hopeful that addressing these gaps will clarify TA's role in diverse rosacea subtypes and refine its clinical application.
References
- Zhang J, Gu D, Yan Y, et al. Potential role of tranexamic acid in rosacea treatment: conquering flushing beyond melasma. Clin CosmetInvestig Dermatol. 2024;17:1405-1412. Published 2024 Jun 14. doi:10.2147/CCID.S473598
- Marson JW, Baldwin HE. Rosacea: a wholistic review and update from pathogenesis to diagnosis and therapy. Int J Dermatol. 2020;59(6):e175-e182. doi:10.1111/ijd.14757
- Kim MS, Chang SE, Haw S, et al. Tranexamic acid solution soaking is an excellent approach for rosacea patients: a preliminary observation in six patients. J Dermatol. 2013;40(1):70-71. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01515.x
- Zhong S, Sun N, Liu H, et al. Topical tranexamic acid improves the permeability barrier in rosacea. Dermatol Sin. 2015;33(2):112–117 doi:10.1016/j.dsi.2015.04.012
- Jakhar D, Kaur I, Misri R. Topical 10% tranexamic acid for erythematotelangiectatic steroid-induced rosacea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86(1):e1-e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2019.12.067
- Bageorgou F, Vasalou V, Tzanetakou V, et al. The new therapeutic choice of tranexamic acid solution in treatment of erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2019;18(2):563-567. doi:10.1111/jocd.12724
- Kwon HJ, Suh JH, Ko EJ, et al. Combination treatment of propranolol, minocycline, and tranexamic acid for effective control of rosacea. Dermatol Ther. 2017;30(3):10.1111/dth.12439. doi:10.1111/dth.12439
- Daadaa N, Litaiem N, Karray M, et al. Intradermal tranexamic acid microinjections: a novel treatment option for erythematotelangiectatic rosacea. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(10):3324-3329. doi:10.1111/jocd.14209